With the development and progress of technology, Bluetooth and Wifi technologies are becoming more and more similar in terms of functions. Similar usage environments and scenarios have made the competition between the two fierce. So who can beat whom? Which one is better, Bluetooth or Wifi technology?

As a radio technology that supports short-range communication between devices (generally within 10m), the core features of Bluetooth are: short range, low cost, and high speed. Bluetooth 4.0 includes three sub-specifications, namely traditional Bluetooth technology, high-speed Bluetooth, and new Bluetooth low-power technology. Bluetooth 4.0 mainly improves battery life, energy saving, and device types. Wi-Fi is a technology that can wirelessly connect terminals such as personal computers and handheld devices. 802.11n has made great innovations in power consumption and management, which can not only extend the battery life of Wi-Fi smartphones, but also be embedded in other devices.
Please note that for the convenience of comparison, the author uniformly uses the currently more popular Bluetooth 4.0 and 802.11n standards for comparison. (Note: The latest Bluetooth version is 4.1, which adds support for wearable devices and IPV6, but this version has not yet been widely popularized. 802.11ac is the successor of 802.11n, and the subsequent 802.11ad and 802.11ae are still being drafted.)
Similarities and differences
Both Bluetooth and WIfi belong to wireless communication network standards and can work in the ISM2.4GHz public frequency band. Bluetooth uses the FHSS method, which generally jumps 1600 times per second, dividing the 83.5MHz frequency band into 79 frequency band channels, each occupying only 1MHz of bandwidth at a time. The protocol used by wifi is the 802.11 standard. Most 802.11 uses the 2.4GHz ISM frequency band, and a few countries use the 5GHz ISM frequency band.
Transmission speed
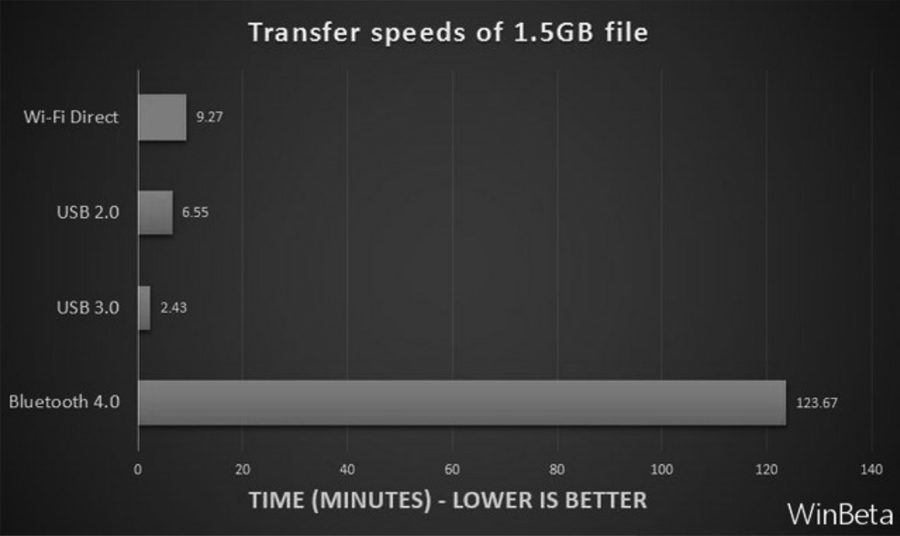
Transmission time comparison (picture from WinBeta)
The theoretical rate of 802.11n can reach up to 600Mbps, while the current mainstream in the industry is 300Mbps. The theoretical peak rate of Bluetooth 4.0 is 25Mbps, supporting ultra-short data packets at a data transmission rate of 1Mbps. Currently, the highest rate of 802.11.ac is 500 Mbit/s, and it is said that the future 802.11.ad will reach the order of Gbit/s, of course, mainly for the range of 10+m (within 1km). In terms of transmission rate, Wifi still has a considerable advantage.



